Over my career, I have developed a few strongly-held design beliefs, and one came up in conversation recently, during a spirited discussion on minimal quality requirements for a[ny] data mart. I hold that the data copied from source to destination must be provably correct and complete with little effort. When agile-ly rolling staged deliverables into production, I may not have all the attributes in place for full flexibility of drill down, but if you have [say] 1248 records in the source system, representing $154,238.54 of transactions, you better have exactly the same amounts in the reporting tool – easily checked with a simple hash total. There should be no inbound filters or transforms – save that stuff for the meta data and/or presentation layer.

How exactly does this relate to “design”?
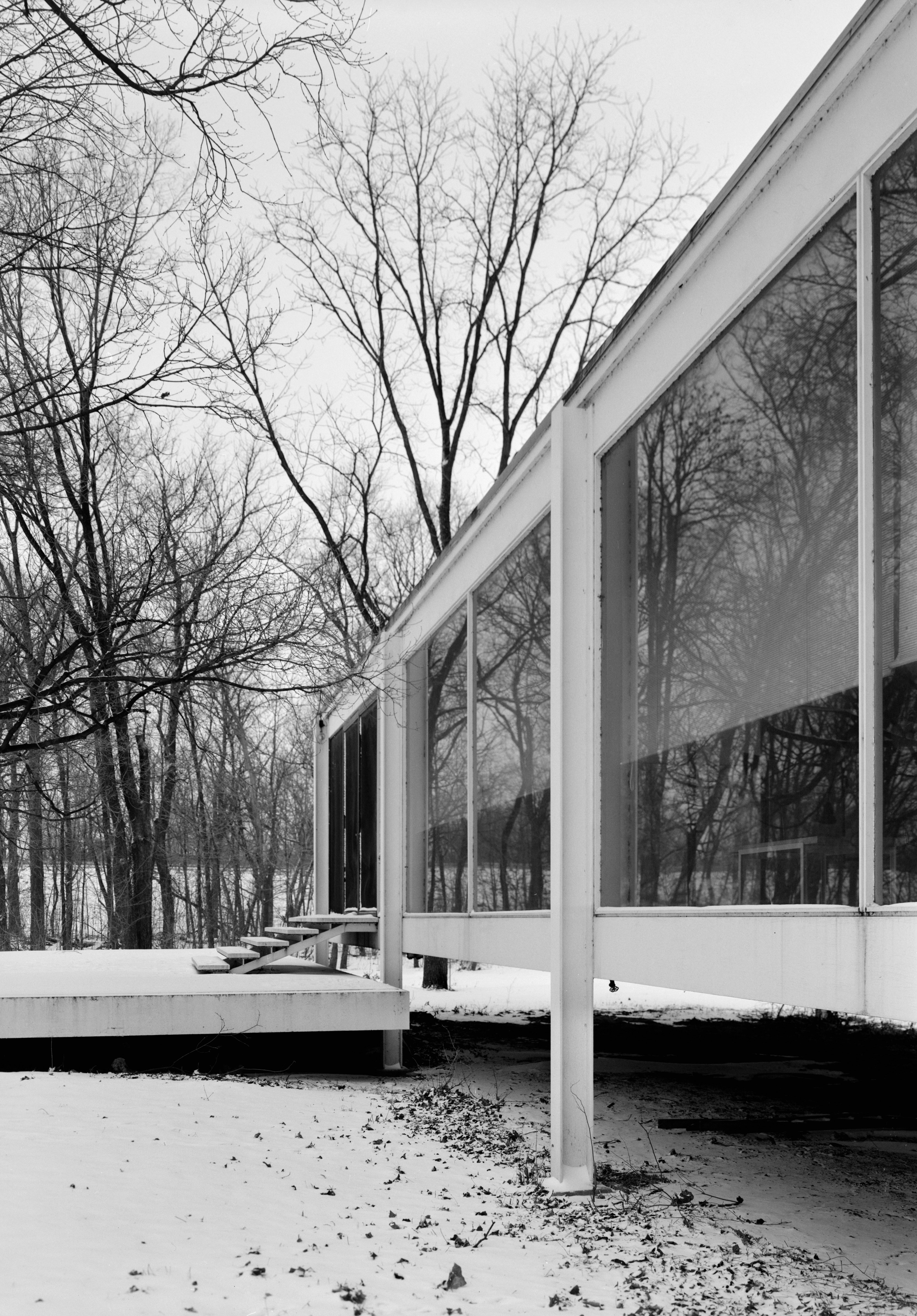
Sounds a bit techie / wonky, I know – but I will find myself obsessing over the details of layout (screens, forms, & slides) and page formatting (specifically for the printed page) – possibly a bit too much, but it’s ultimately about user acceptance. If an presentation / document / report / application looks like it was thrown together, with extraneous messaging or ornamentation – well, people will use that as an excuse to write the piece off as complicated and/or incomplete. Often, when introducing new ideas, products, systems, metrics, and/or processes, you are introducing significant change in people’s lives. There is always natural resistance to change – resistance that looks for anything to latch onto and call into question. Like rubbing a cotton ball over a rough surface – teeny imperfections will snag & fluff their attention, and distract from the view.
It’s much the same with my data mart example; these analytical wonders often expose uncomfortable truths or (more likely) opportunities that were there all along, just hidden from view. For the unbelievers, or those wishing to delay the [potentially] bad news, any excuse to question the validity and accuracy of the data will do. Do yourself a favor – a simple hash total proving that 100% of the data got from point A to point B helps limit the fingerpointing and focus debugging attention on a simpler set of scapegoats.
Change Manage the “Big Stuff”
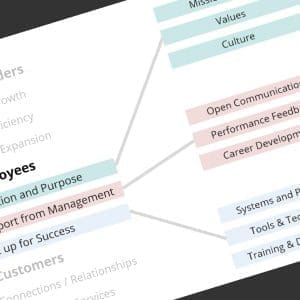
Pay attention to the details of the design, how everything fits together – and obsess over the nits that will detract from the core message. This pays off big when nothing happens. Well, maybe nothing that you don’t want; communication with zero distractions lets you focus on the elephants in the room, where your change management energies will be best spent.
The design is successful when all the angsty conversation is about the new process you are introducing, the meaning behind the metrics – not the fact that the type is too small or the multiple fonts make something hard to read – or the numbers just don’t add up.





This Post Has 0 Comments